Damage to fragile environments: farming and desertification in the Sahel
Management issues
Underlying Causes
| Cause | Effect |
|---|---|
| Climatic | • Droughts are now more common
• High temperatures cause a high rate of evapotranspiration • Rainfall is infrequent but intense, causing soil erosion |
| Over population | • Overgrazing
• Overcultivation • Deforestation • Change in traditional farming practices. Nomads have adopted a more sedentary (settled) lifestyle with no change in traditional herding practices |
| Growth of Game Parks for tourism or of commercial farming interests. Cash crops take over the prime lands | • Reduced grazing land
• Nomads have adopted a more sedentary (settled) lifestyle with no change in herding practices • Overgrazing, overcultivation and deforestation |
| Cattle represent wealth and confer social prestige | • Overgrazing |
 |
| The effects of overgrazing and the need to collect ever increasing quantities of fuel wood from the area surrounding a settlement |
Specific Causes
| Causes | Effects |
|---|---|
| Overgrazing | • Grass is unable to regrow
• Soil erosion • Desertification |
| Overcultivation
Farmers forced to grow crops on marginal land |
• The continual use of the soil leads to loss of
soil structure
• Soil erosion • Desertification |
| Deforestation
Trees are removed for fuel and to clear land for crops |
• Trees are removed for fuel
• Deforestation leads to soil erosion and:
|
Click for graphic links:
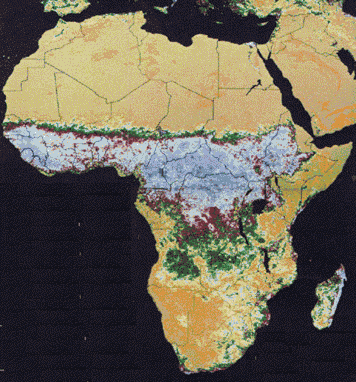
NASA AVHRR (Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer)
Image from 1986 shows the sharp boundary between the deserts to the North and
the dense forests to the South on the Sahel |
