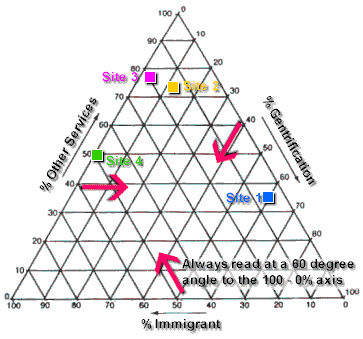
Data Presentation: Triangular Graphs
Example: Service structure data for selected urban areas can be plotted on a three-sided triangular graph. The important features of a triangular graph are:
-
Each axis is divided into 100, representing percentages.
-
From each 100-0% axis, lines are drawn at angles of 60 degrees to carry the values.
-
The data used must be in the form of three components, each component representing a percentage value, and the three component percentage values must add up to 100 per cent.
The position of the plots indicates the relative dominance of each of the three components and the value of the graph arises in giving a quick visual comparison of contrasting component dominance for different areas. It is particularly useful in identifying changes over time, since a position on the graph will change as the relative dominance of the components change.
The graph can be used to show contrasting service structures for 4 locations in El Raval, an inner-city area of Barcelona which has been the subject of radical urban reform. The choice of the three graph components is important and must be in the context of the investigation. An example of data from one location (El Raval Site 2) is shown in map 1 below, and this has been used along with data from three other sites (1,3 and 4) to compile the triangular graph.
|
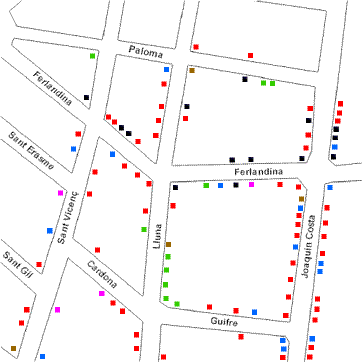
Map 1: Service Structure in El Raval, Site 2 |
Service Structure Data Summary Chart for Sites1-4
| El Raval Service Structure | ||||
| Service | Site 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | Site 4 |
| % Gentrification | 60 | 11.4 | 3 | 0 |
| % Immigrant Services | 5 | 15.2 | 20 | 50 |
| % Other Local Services | 35 | 73.4 | 76 | 50 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
|
Data example is for training purposes only. Its accuracy cannot be guaranteed. |
|
Triangular graph to show the contrasting service structure for four areas of El Raval
![]() Triangular Graph Online Constructor
Triangular Graph Online Constructor