Data Presentation: Pie Charts
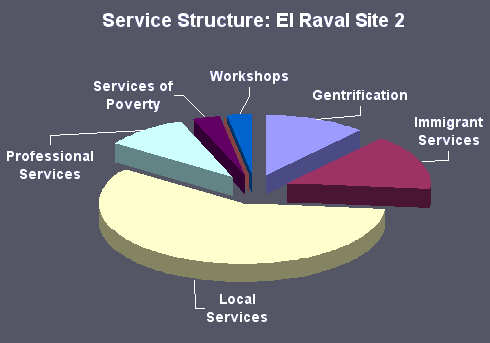
Example: El Raval service structure data for Site 2 with percentage values.
|
Map 1: Service Structure in El Raval, Site 2 |
Service Structure Data Summary Chart Site 2
| El Raval Site 2 | ||
| Service | Number | % |
| Gentrification | 12 | 11.4 |
| Immigrant Services | 16 | 15.2 |
| Local Services | 61 | 58.1 |
| Professional Services | 10 | 9.5 |
| Services of Poverty | 3 | 2.9 |
| Training Centres | 0 | 0 |
| Workshops | 3 | 2.9 |
| Total | 105 | 100 |
| Size of area: 0.25 x 0.25 km² = 0.0625 km² | ||
| No. of businesses per km² = 1,680 | ||
|
Chart to show The Structure of Services in El Raval Site 2
Advantages
-
display relative proportions of multiple classes of data
-
size of the circle can be made proportional to the total quantity it represents
-
summarize a large data set in visual form
-
be visually simpler than other types of graphs
-
permit a visual check of the reasonableness or accuracy of calculations
-
require minimal additional explanation
-
be easily understood due to widespread use in business and the media
Disadvantages
-
do not easily reveal exact values
-
Many pie charts may be needed to show changes over time
-
fail to reveal key assumptions, causes, effects, or patterns
-
be easily manipulated to yield false impressions